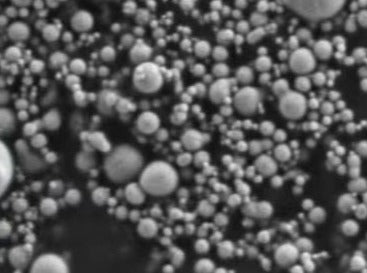
MSE PRO Nickel (Ni) Nanopowder, 40nm, ≥99.9% (3N) Purity, 100g
SKU: PO7020
MSE PRO™ Nickel (Ni) Nanopowder, 40nm, ≥99.9% (3N) Purity, 100g
- Product Number: PO7020
- Formula: Ni
- CAS Number: 7440-02-0
- Molecular Weight: 58.69g/mol
- Density: 8.9g/cm³ at 25°C
- Melting Point: 1453°C
- Particle Size: 40nm
- Purity: ≥99.9% 3N
- Appearance: Black powder
Applications:
Nickel nanoparticles (Ni NPs) have been investigated for various potential applications due to their superior ferromagnetic properties such as magneto-crystalline anisotropy, high coercive forces, and chemical stability. The strong magnetic response as well as interfacial properties make Ni NPs suitable for catalysts in the separation of emulsions, separation, cleaning of the oil spills, purification of water, and the separation of impurities from samples. Unique properties of Ni NPs make them ideal candidates in various technological fields such as catalyst, battery manufacture, novel ink for nanotube-printing, field-modulated gratings and optical switches, direct immobilization of biomolecules.
Notes: More detailed product information including SDS, certificate of analysis (COA), customized order are available upon request.
| Impurity Analysis (wt%) by ICP | |||
| Co | ≤0.04 | Fe | ≤0.03 |
| Cu | ≤0.02 | Pb | ≤0.002 |
| S | ≤0.003 | Si | ≤0.004 |
| Zn | ≤0.002 | Ca | ≤0.02 |
| Mg | ≤0.005 | Mn | ≤0.011 |
| C | ≤0.021 | Hydrogen Loss | ≤0.21 |
References:
