MSE PRO 1% Silver (Ag) Nanoparticle Water Dispersion, 160-180nm, >99.99% Purity
SKU: CM2025
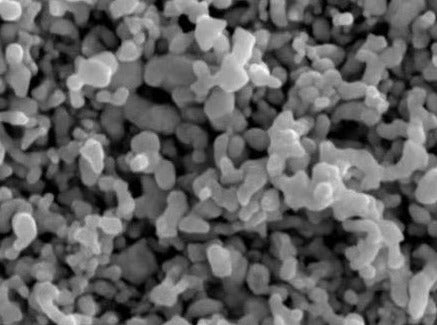
MSE PRO™ 1% Silver (Ag) Nanoparticle Water Dispersion, 160-180nm, >99.99% Purity
Silver (Ag) nanoparticles have received considerable attention owing to their attractive physicochemical properties. The surface plasmon resonance and large effective scattering cross section of individual silver nanoparticle make them ideal candidates for molecular labeling where phenomena such as surface enhanced Raman scattering can be exploited. Recent studies have shown that silver nanoparticles with highly branched amphiphilically modified polyethyleneimines can adhere to polar substrates for antimicrobial coating application. Silver nanoparticle can also be applied to ink-jet conductors.
Technical Specifications:
| Product Name | Silver Nanoparticle |
| SKU# |
CM2025: 250 mL CM2026: 500 mL |
| CAS# | 7440-22-4 |
| Chemical Formula | Ag |
| Average Primary Particle Size | 160-180 nm |
| Appearance | Black powder dispersion |
| Purity | >99.99 % |
| Shape | Spherical |
| Concentration | 1 % |
| Solvent | Water |
| Impurity |
|
References:
[2]: Microwave plasma synthesis of silver nanopowders. Materials Letters 59, no. 8-9 (2005): 905-908.
