Total Superoxide Dismutase (T-SOD) Activity Assay Kit (WST-1 Method)
SKU: E-BC-K020-M-500
Total Superoxide Dismutase (T-SOD) Activity Assay Kit (WST-1 Method)
| SKU # | E-BC-K020-M |
| Detection Instrument | Microplate reader (440-460 nm, optimum wavelength: 450 nm) |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric method |
Product Details
Properties
| Synonyms | T-SOD |
| Sample Type | Serum, plasma, hydrothorax, ascites, urine, cells, tissue |
| Sensitivity | 0.2 U/mL |
| Detection Range | 0.2 -14.4 U/mL |
| Detection Method | Colorimetric method |
| Assay type | Enzyme Activity |
| Assay time | 30 min |
| Precision | Average inter-assay CV: 3.700% | Average intra-assay CV: 2.900% |
| Other instruments required | Micropipettor, Multichannel pipettor, Vortex mixer, Incubator |
| Other reagents required | Normal saline (0.9% NaCl) or PBS (0.01 M, pH 7.4) |
| Storage | Reagent 3: -20℃, others: 2-8℃ |
| Valid period | 12 months |
Dilution of Sample
The optimal sampling volume are different for different species, the SOD also are different for different samples. It is recommended to take 2~3 samples to do a pre-experiment, diluting a series of diluent and determine the dilution factor when the SOD inhibition ratio is 25%~65% (the optimal inhibition ratio is the range of 40%~60%.) before formal experiment.
The recommended dilution factor for different samples is as follows (for reference only):
| Sample type | Dilution factor |
| Human serum | 3-5 |
| Rat serum | 20-30 |
| Urine | 1 |
| Human hydrothorax | 2 |
| Cell culture supernatant | 2-3 |
| 10% Rat liver tissue homogenate | 340-370 |
| 10% Rat heart tissue homogenate | 80-100 |
| 10% Rat kidney tissue homogenate | 100-120 |
| 10% Rat brain tissue homogenate | 50-100 |
| 10% Plant tissue homogenate | 5-10 |
| HepG2 cells (3 mgprot/mL) | 30-40 |
Note: The diluent is normal saline (0.9% NaCl) or PBS (0.01 M, pH 7.4).
Detection Principle
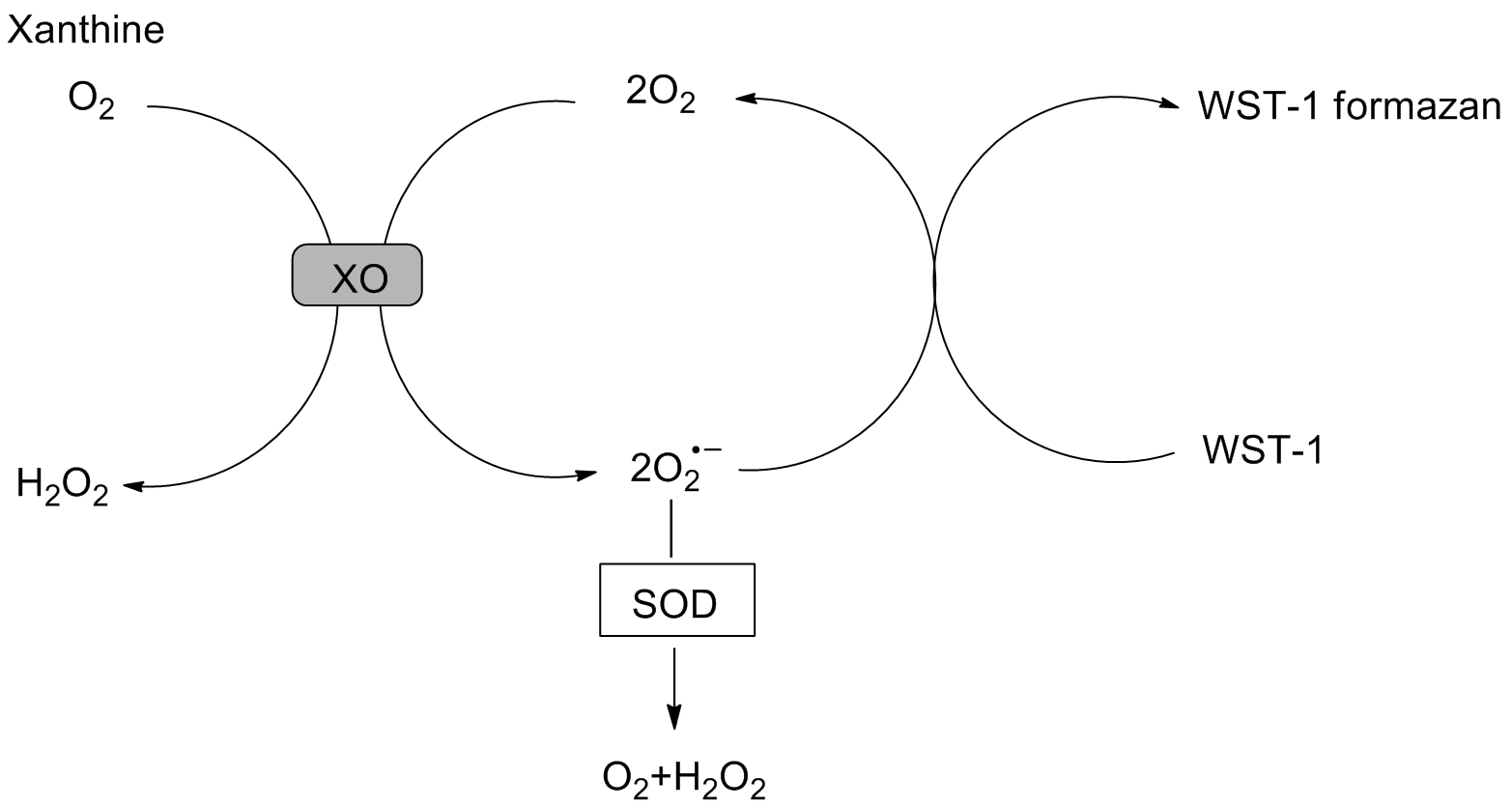
The activity of SOD was measured by WST-1 method in this kit and the principles of the WST-1 is as follows. Xanthine Oxidase (XO) can catalyze WST-1 react with O2.- to generate a water-soluble formazan dye. SOD can catalyze the disproportionation of superoxide anions, so the reaction can be inhibited by SOD, and the activity of SOD is negatively correlated with the amount of formazan dye. Therefore, the activity of SOD can be determined by the colorimetric analysis of WST-1 products.
Kit Components & Storage
| Item | Component | Size 1 (48 T) | Size 2 (96 T) | Storage |
| Reagent 1 | Buffer Solution | 12 mL × 1 vial | 24 mL × 1 vial | 2-8℃, 12 months |
| Reagent 2 | Substrate Solution | 0.07 mL × 1 vial | 0.14 mL × 1 vial | 2-8℃, 12 months shading light |
| Reagent 3 | Enzyme Stock Solution | 0.15 mL ×1 vial | 0.3 mL ×1 vial | -20℃, 12 months |
| Reagent 4 | Enzyme Diluent | 1.5 mL × 1 vial | 1.5 mL × 2 vials | 2-8℃, 12 months |
| Microplate | 96 wells | No requirement | ||
| Plate Sealer | 2 pieces | |||
Note: The reagents must be stored strictly according to the preservation conditions in the above table. The reagents in different kits cannot be mixed with each other. For a small volume of reagents, please centrifuge before use, so as not to obtain sufficient amount of reagents.
Technical Data:
Parameter:
Intra-assay Precision
Three human serum samples were assayed in replicates of 20 to determine precision within an assay (CV = Coefficient of Variation).
| Parameters | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 |
| Mean (U/mL) | 1.20 | 8.40 | 12.50 |
| %CV | 3.2 | 3.0 | 2.5 |
Inter-assay Precision
Three human serum samples were assayed 20 times in duplicate by three operators to determine precision between assays.
| Parameters | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 |
| Mean (U/mL) | 1.20 | 8.40 | 12.50 |
| %CV | 3.4 | 3.8 | 3.9 |
Recovery
Take three samples of high concentration, middle concentration and low concentration to test the samples of each concentration for 6 times parallelly to get the average recovery rate of 98%.
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | |
| Expected Conc. (U/mL) | 3.5 | 9.6 | 13 |
| Observed Conc. (U/mL) | 3.5 | 9.1 | 12.6 |
| Recovery rate (%) | 99 | 95 | 97 |
Sensitivity
The analytical sensitivity of the assay is 0.2 U/mL T-SOD. This was determined by adding two standard deviations to the mean O.D. obtained when the zero standard was assayed 20 times, and calculating the corresponding concentration.



