MSE PRO Solid-Core Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Powder
SKU: MS0255
MSE PRO™ Solid-Core Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Powder
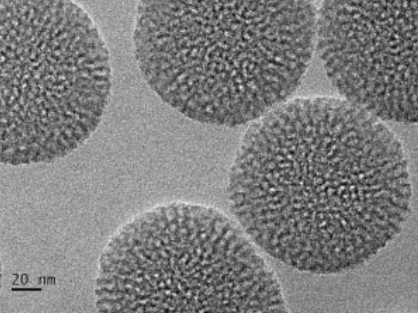
MSE SUPPLIES offers a Solid-Core Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Powder with a layered structure, prepared through the soft template method in an oil-water two-phase reaction system, featuring center-radial and dendritic mesoporous channels. As an inorganic material, it has three-dimensional dendrites, making it highly biocompatible and suitable for various clinical applications, such as catalysis, separation, adsorption, and biomedicine.
Technical Specifications:
| CAS | 7440-21-3 | |
| Package |
500 mg: MS0255 1 g: MS0256 |
500 mg: MS0257 1 g: MS0258 |
| Average particle size | 140-180 nm | 80-120 nm |
| Specific surface area | ~500 m2/g | ~765.7 m2/g |
| Pore volume | 0.48 cm³/g | 1.12 cm³/g |
| Average pore size | 3-4 nm | 5-7 nm |
| Appearance | White powder | White powder |
| Storage | Store sealed and light-protected at room temperature. | |
Buy Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Powder at MSE Supplies for the best prices on the market. For bulk orders, please contact us for a quote.